Overview
Palmyrah Development Board produces a variety of edible and non-edible Palmyrah based products. Edible products are mainly from the fruit and other items of Palmyrah tree are utilized for the non-edible products and for the production of Beverage. The Production Division of the PDB is the statutory top organization established under the provisions of the Coconut Development Act No. 46 of 1971 (amended by Act No. 24 of 1975). It is responsible for
- Engaging in the regulation, control, supervision, direction, management and inspections of the manufacture, packing storing, transport, sale, purchase, import and export of the palmyrah product.
- Inspection, supervision, regulation and control of factories, stores, yards, buildings premises, equipment and machinery intended to be used for the manufacture, packing or storing of palmyrah products.
- This website aims to act as a bridge for manufacturing Palmyrah products and establishing strong links with producer networks.
Product Categories
1. Edible Products
2. Non-Edible Products
a. Sap based products
- Non fermented products: Sweet sap, Treacle, Jaggery
- Fermented products: Bottled toddy, Wine, Vinegar
b. Fruit based products
- Nungu
- Concentrated Pulp
- Beverages (Palm Crush, Instant Soft Drink)
- Panattu
- Pani Panattu
- Jam
c. Palmyrah Food Products
- Panangai Paniyaram (Kevum)
- Palm Chocolate
- Palm Oil Cake
d. Tuber based products
- Boiled Dried Odiyal
- Seeval Dried Odiyal
- Boiled Dried Odiyal Round Chips
- Odiyal flour
- Boiled Odiyal flour
e. Leaf based products
f. Fiber based products
g. Timber based products
Production centers of PDB
| District | Jaggery | Pulp | Non Fermented drink | Tuber based Product & Packaging |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jaffna | Singainagr | Kaithady | Karainagar | |
| Killinochchi | Kowtharimunai | |||
| Mannar | Kaddukaran Kudirupu | Padappaddi | ||
| Tharavankottai | ||||
| Padappaddi | ||||
| Trincomalae | Verothayanagar | |||
| Batticaloa | Muhathuvaram | |||
| Puttalam | Kalpitiya |
Production centers of PDCS
| District | PDCS | Toddy | Pulp | Jaggery | Flour |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jaffna | Kopay | ✖ | |||
| Velanai | ✖ | ||||
| Analai theevu | ✖ | ||||
| Karainagar | ✖ | ||||
| Kayts | ✖ | ||||
| Changanai | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | ||
| Manipay | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | ||
| Kondavil | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | ||
| Thellippali | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | ||
| Pandaththarippu | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | |
| Atchchuvely | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | ||
| Karaveddy | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | ||
| Pointpitro | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | ||
| Chavachacheri | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | ||
| Killinochchi | Pallai | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | |
| Poonakari | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | ||
| Killinochchi | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | ||
| Mullaitheevu | Mullai west | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | |
| Mullai east | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | ||
| Mullai north | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | ||
| Mullai south | ✖ | ||||
| Vizuvamadu | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | ||
| Oddusuddan | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | ||
| Puthukkudigiruppu | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | |
| Vavuniya | Nedunkerni | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | |
| Puliyankulam | ✖ | ✖ | |||
| Vavuniya | ✖ | ||||
| Mannar | Mannar west | ✖ | ✖ | ||
| Mannar east | ✖ | ✖ | |||
| Nanaddan | ✖ | ✖ | |||
| Adampan | ✖ | ✖ | |||
| Uyilankukam | ✖ | ✖ |
Functions
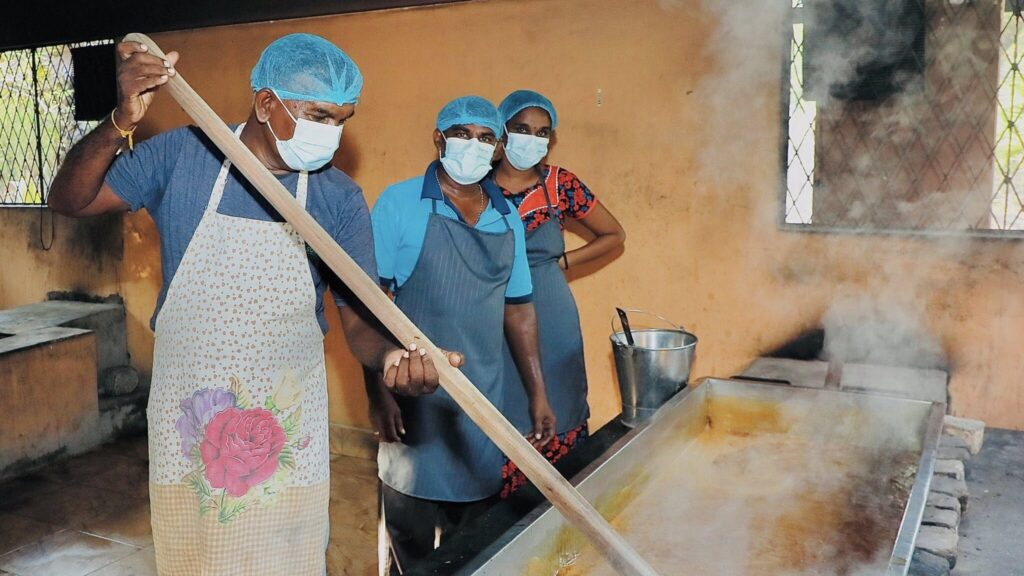
1. Raw Material Processing
Raw material processing involves the initial steps to transform palmyrah resources into usable forms. This stage focuses on:
- Collection of Resources: Harvesting sap, collecting fruits, and fibers from the palmyrah tree during the season.
- Sap Processing: Fresh sap is processed to create products such as Toddy, Sweet sap, Treacle, and Jaggery.
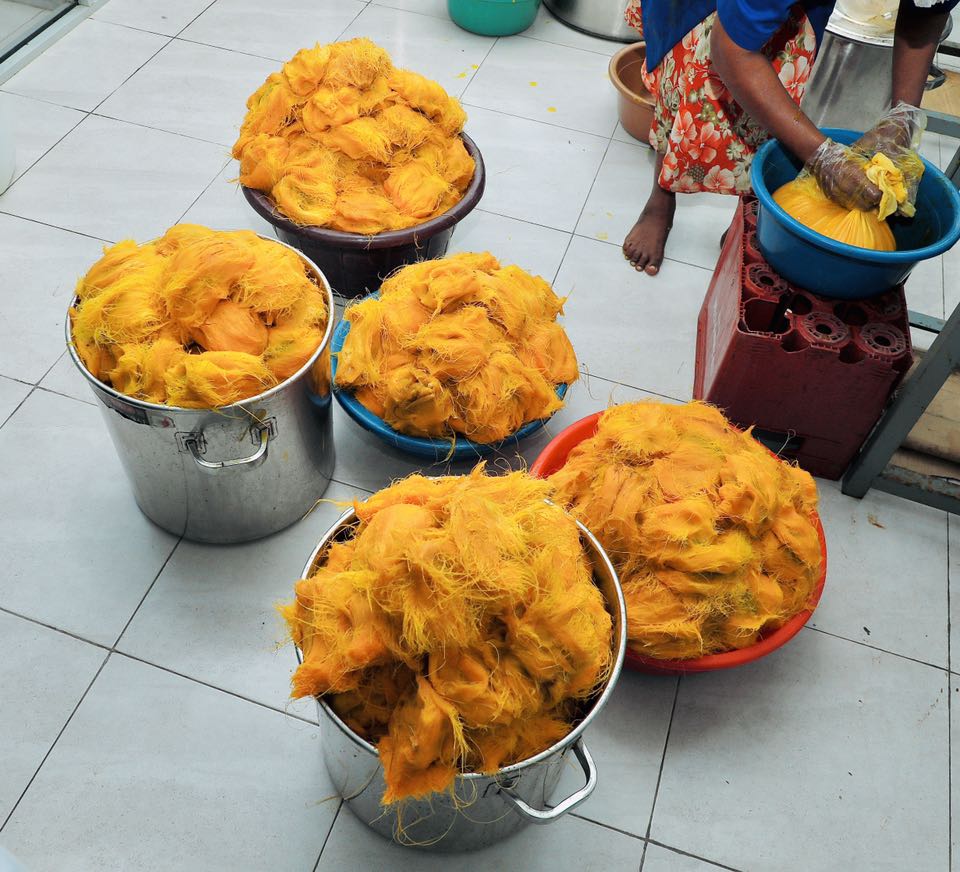
- Fruit Processing: Palmyrah fruits are collected to extract pulp, which can be preserved for making cordial, juices, and jams.
- Fiber Extraction: The fibrous material from the tree or fruits is extracted and processed.
- Tuber: Tubers are cleaned, sliced, and dried to create flour.
2. Product Development and Manufacturing
This function focuses on converting raw materials into a diverse range of Palmyrah-based products, ensuring value addition. Key aspects include:
- Food Products: Developing consumables like Jaggery, candy, treacle, and porridge mixes.
- Beverages: Creating non-alcoholic drinks like cordial RTS or fermented beverages such as toddy.
Product development involves testing, packaging, and branding to appeal to target audiences and meet regulatory standards.
3. Quality Control and Standardization
Ensuring the quality and safety of palmyrah products is essential for consumer satisfaction and market compliance. The steps include:
- Hygiene and Safety: Maintaining cleanliness in processing centers to prevent contamination of food and beverage products.
- Chemical and Nutritional Analysis: Testing for nutritional content, shelf life, and absence of harmful substances like pathogens or heavy metals.
- Adherence to Standards: Complying with local and international regulations, such as ISO standards, HACCP (Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point), or food safety laws.
- Certification: Obtaining certifications (e.g., organic,) to enhance product credibility in premium markets.
- Consistency in Production: Using standardized procedures and recipes to ensure uniform taste, quality, and appearance across batches.
- Packaging Quality: Ensuring that packaging materials are durable, eco-friendly, and suitable for preserving product freshness.
Contact Us
Mr. Hubert Anthony
Manager (Production) – Acting
Tel: 021 2222034
Fax: 021 2224154
E-Mail: slpdbho@gmail.com