The “Palmyrah Tree”
The palmyrah palm (Borassus flabellifer), often referred to as the “tree of life,” is a vital traditional crop that plays a significant role in the livelihood development of people in regions where it grows. Found naturally in countries like Sri Lanka, India, Indonesia, Nepal and other tropical areas, this hardy palm thrives without the need for irrigation, fertilizers, or pesticides, making it a sustainable and low-maintenance crop compared to others like coconut.
Slow growing perennials have no distinguishing features to identify the sex until flowering. The palm commences flowering only after 15 to 20 years of maturity. Hardy and irregular growth habit of the non-branching trunk makes it difficult for the climber to climb the tree for collection of sweet toddy and toddy.
Ecologically, the palmyrah palm provides habitats for various flora and fauna, contributing to biodiversity. Its robust root system helps preserve underground water tables, control soil erosion, and act as a natural windbreak, protecting the environment from harsh climatic conditions. This multifaceted tree also supports numerous industries, producing fruits, sap, fibers, timber, and leaves that are used in food, construction, crafts, and more.
Truly a marvel of nature, the palmyrah palm exemplifies resilience, sustainability, and resourcefulness, making it a cornerstone of traditional agricultural and ecological systems.

• Implementation of annual palmyrah seed /seedling plantations and progress reporting
• Control of illegal palmyrah tree felling
• Maintenance and intercropping of model plantation lands
• Regulating management of palmyrah plantations
• Conducting studies on plantation management and agronomy
• Planning and Project coordination
Palmyrah Plantation activities
Establishment and maintenance of Palmyrah Plantation is one the mandatory activity of PDB. Restoration of Palmyra while resulting in raw material availability for agro – based food and other consumer items would also be a boom to the environment. Palmyrah Development Board (PDB) being the only state organization engaged in palmyrah industry focuses its fullest attention in increasing the palmyrah vegetation and in protecting the existing palmyrah trees. In this regard annual planting program was implemented during the period of October to December.
| Seeds Planted During Last Three Years by PDB | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Districts | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 |
| Jaffna | 121,685 | 50,400 | 71,600 |
| Mannar | 81,600 | 55,000 | 52,520 |
| Vavuniya | 25,030 | 145,000 | 10,020 |
| Killinochchi | 41,900 | - | 7,500 |
| Mullaithivu | 74,700 | 125,000 | 3,750 |
| Trincomalee | 48,870 | - | 24,000 |
| Batticaloa | 58,173 | 100,000 | 36,400 |
| Ampara | 10,000 | 25,000 | 78,600 |
| Total | 461,958 | 500,400 | 284,390 |
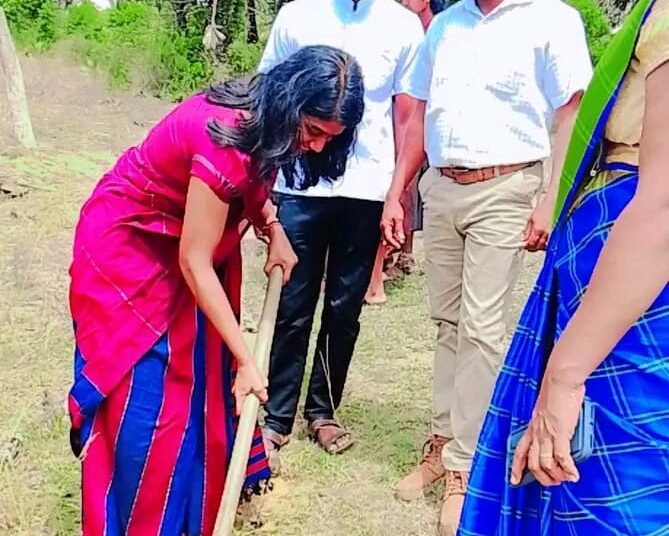
Island-wide Palmyrah Seed Planting Programs
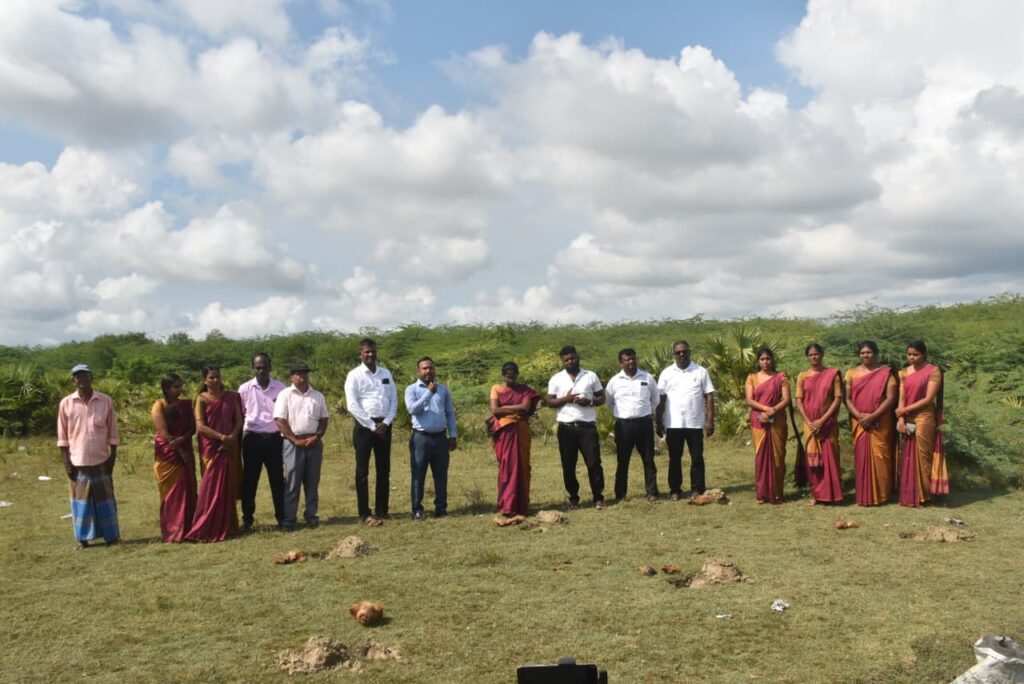
Palm Seed Planting Programme Launched in Poonakary Division, Kilinochchi
The planting of 5,000 palmyrah seeds commenced on 12.11.2025 in the villages of Kautharimunai and Manniththalai in the Poonakary Divisional Secretariat area, with active participation from the local communities. The event was attended by Assistant Divisional Secretary Mrs. Parthiban Krusha, Grama Niladhari Rajagopal, Grama Niladhari Assistants, Senior Planning Officer Mayoon, officers of the Palmyrah Development Board, and community leaders.
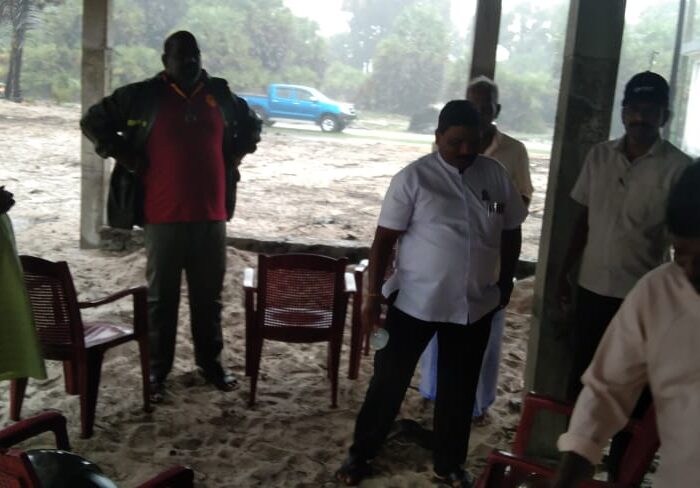
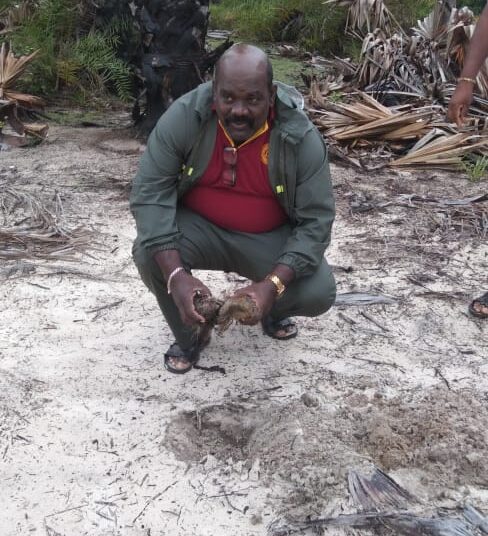
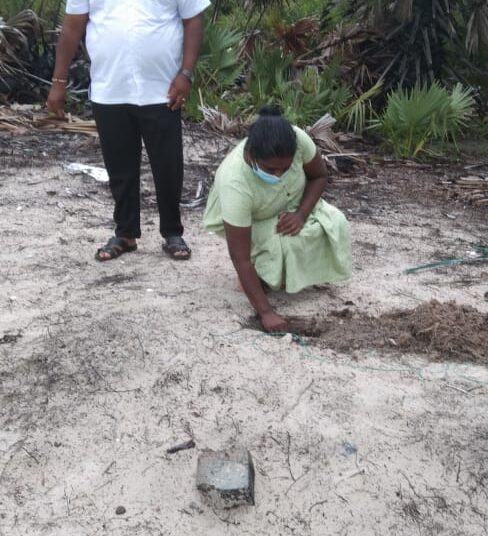
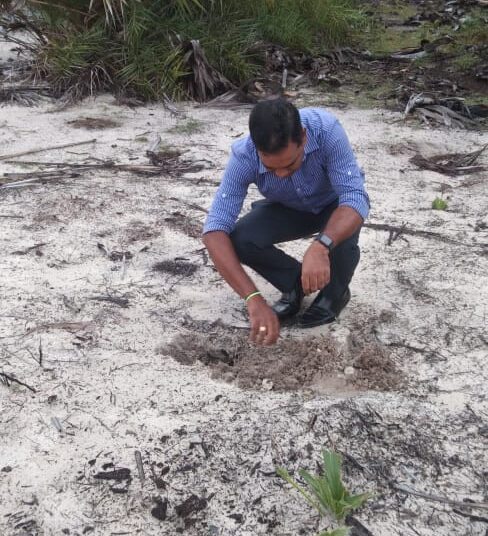
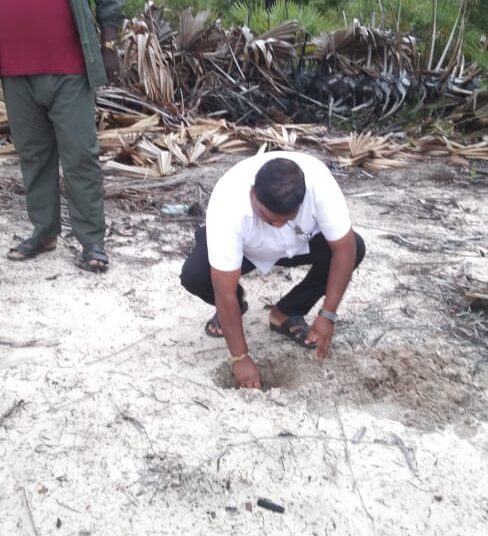





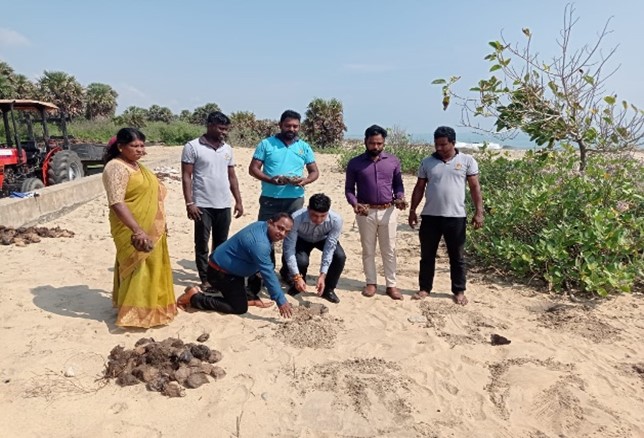
Declaration of “Palmyrah Seed Planting Month of October” at Manmunai North Divisional Secretariat, Batticaloa
As a continuation of this initiative, today (18.10.2025), a program to plant an additional 250 palmyrah seeds was inaugurated at the same coastal site, with the participation of senior officers and staff of the Palmyrah Development Board serving across the island.
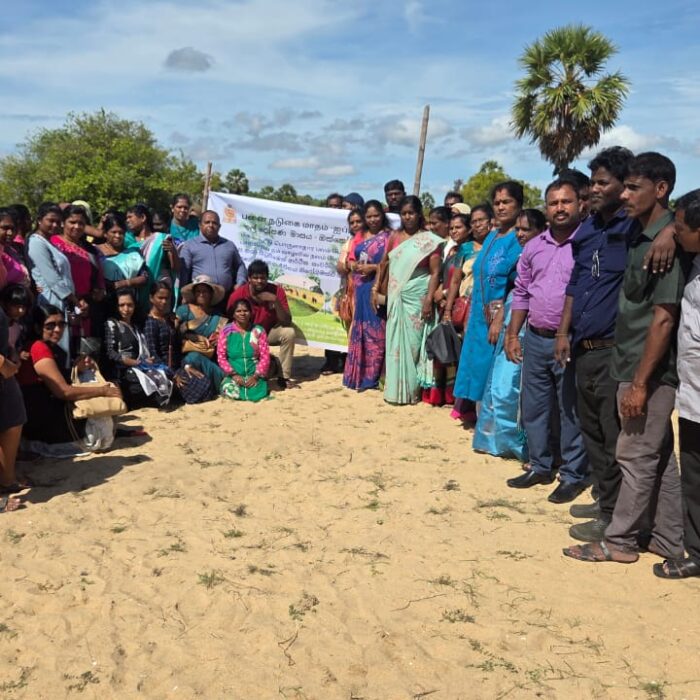
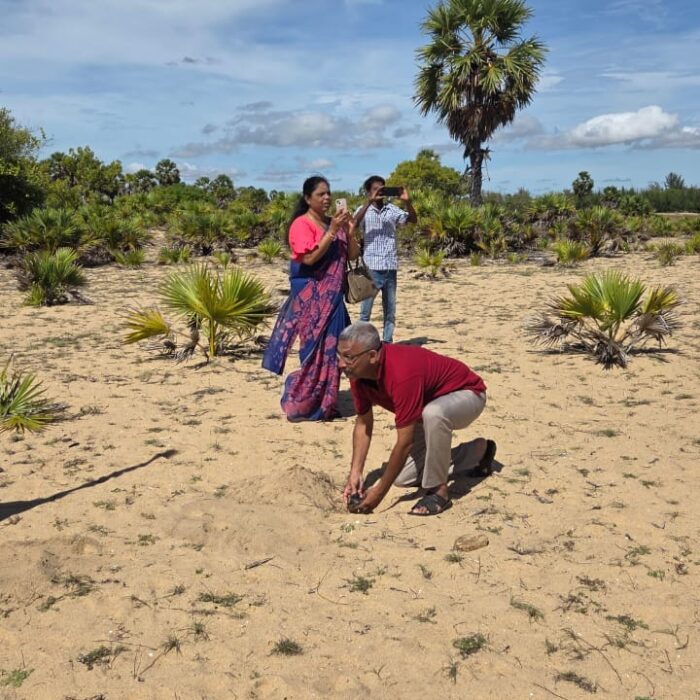
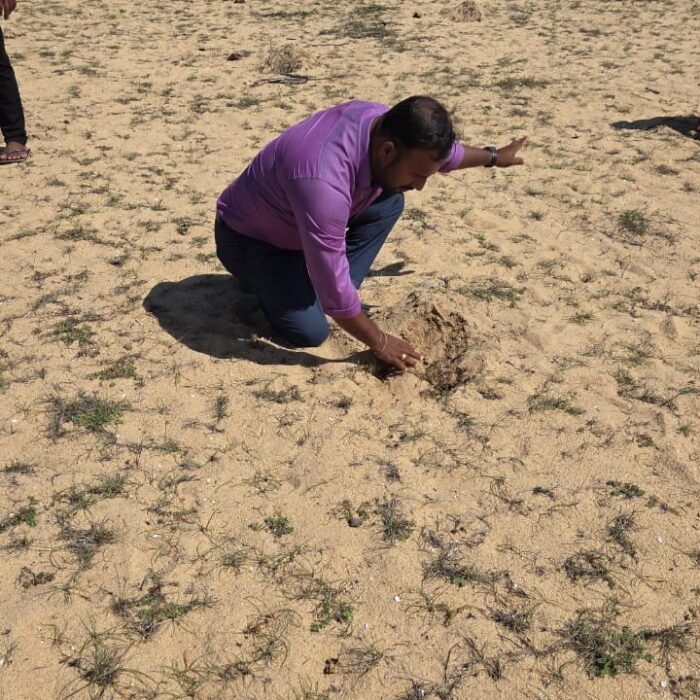
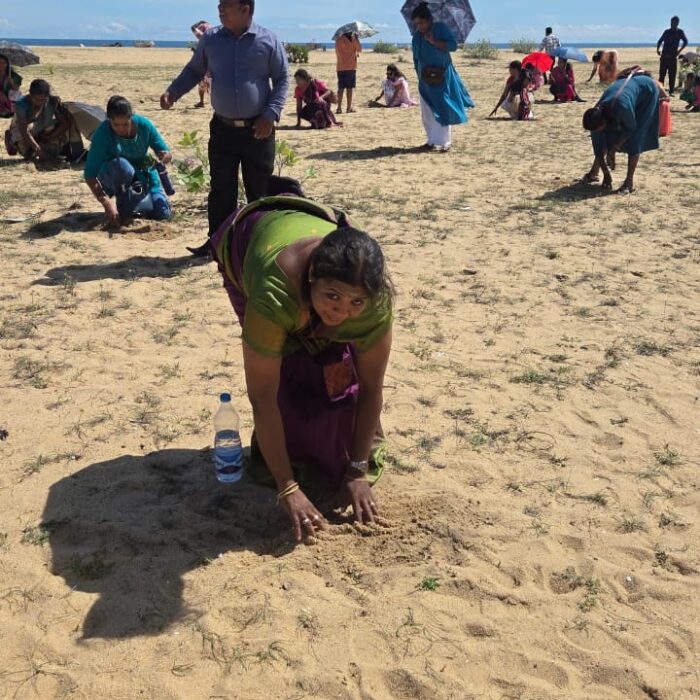
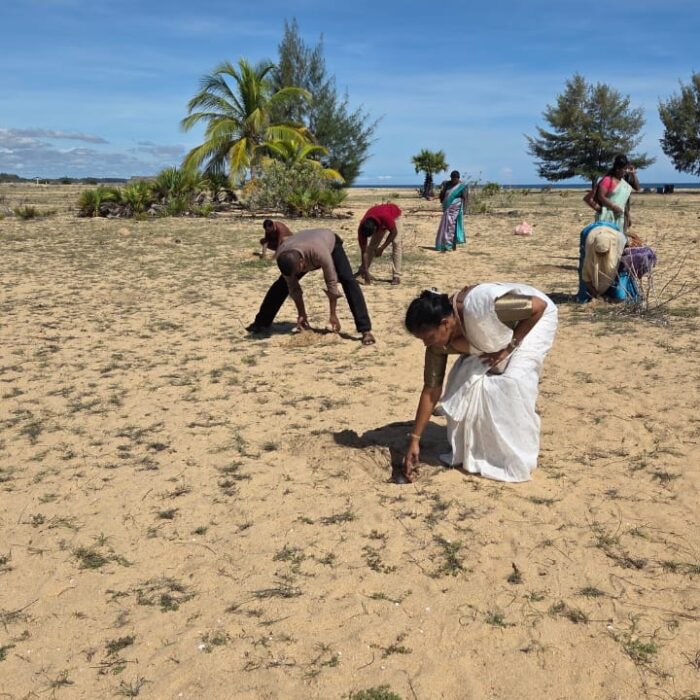





Declaration of “Palmyrah Seed Planting Month” at Karaveddy Divisional Secretariat, Jaffna
8,000 palmyrah seeds will be planted within the Karaveddy Divisional Secretariat area. As the first phase, a program to plant 4,000 palmyrah seeds on state land in Maththony village was officially launched today (14.10.2025).





Palm Seed Planting Programme Launched in Poonakary Division, Kilinochchi
The planting of 5,000 palmyrah seeds commenced on 12.11.2025 in the villages of Kautharimunai and Manniththalai in the Poonakary Divisional Secretariat area, with active participation from the local communities. The event was attended by Assistant Divisional Secretary Mrs. Parthiban Krusha, Grama Niladhari Rajagopal, Grama Niladhari Assistants, Senior Planning Officer Mayoon, officers of the Palmyrah Development Board, and community leaders.





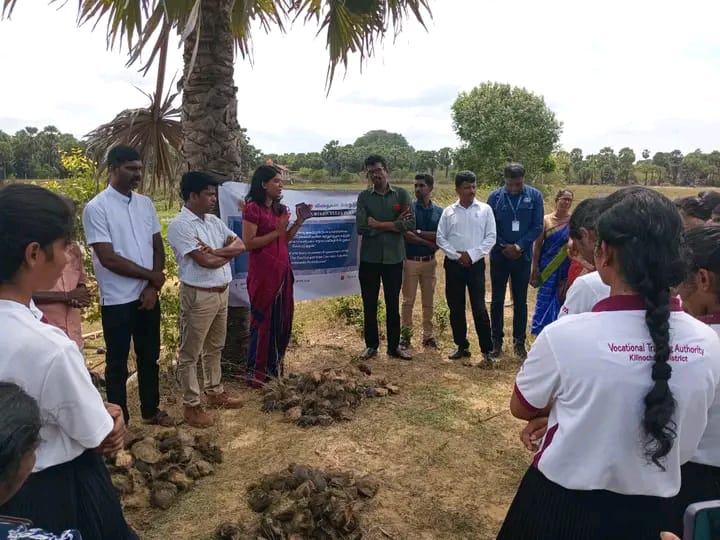
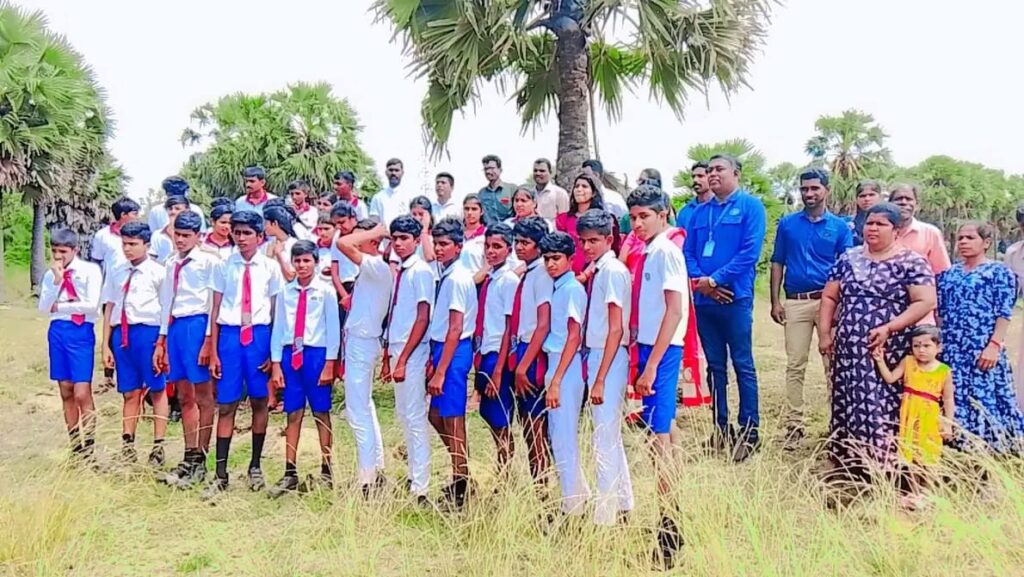
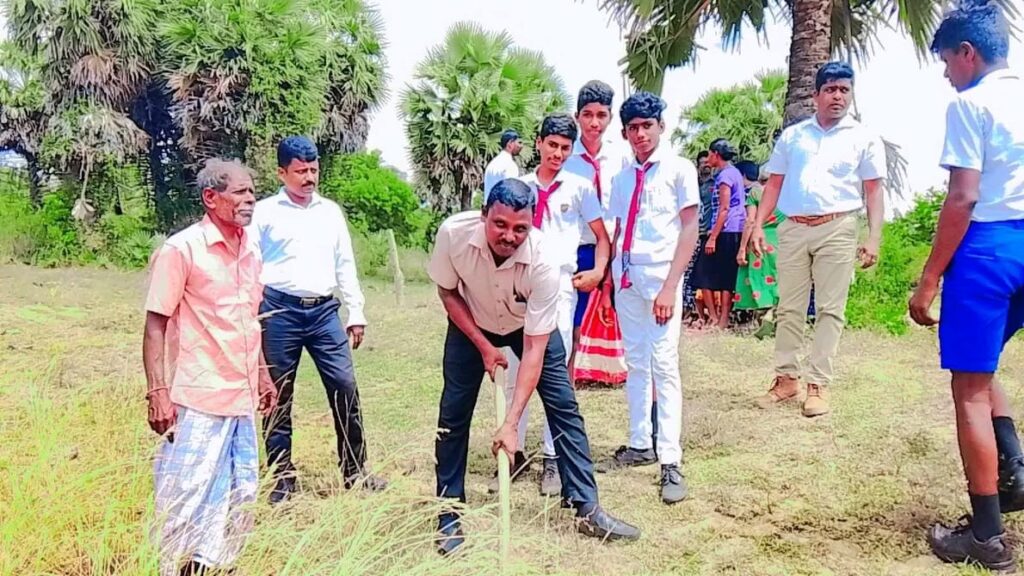
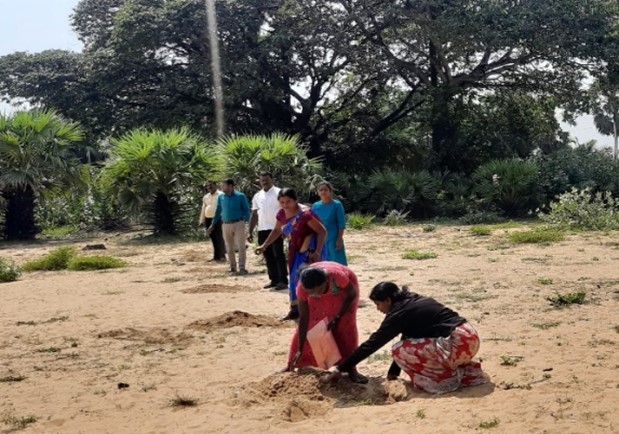
2,000 Palmyrah Seeds Planted in Palaippradesha, Mookamalai Village
On 18th September 2025, the first phase of planting 2,000 Palmyrah seeds was carried out at Mookamalai Village in the Palai Pradesha Secretariat Division, organized by the HDO organization.
The event was attended by the Assistant Divisional Secretary, representatives of HDO, VTA, and Halo Trust, as well as a large number of school students and community members.








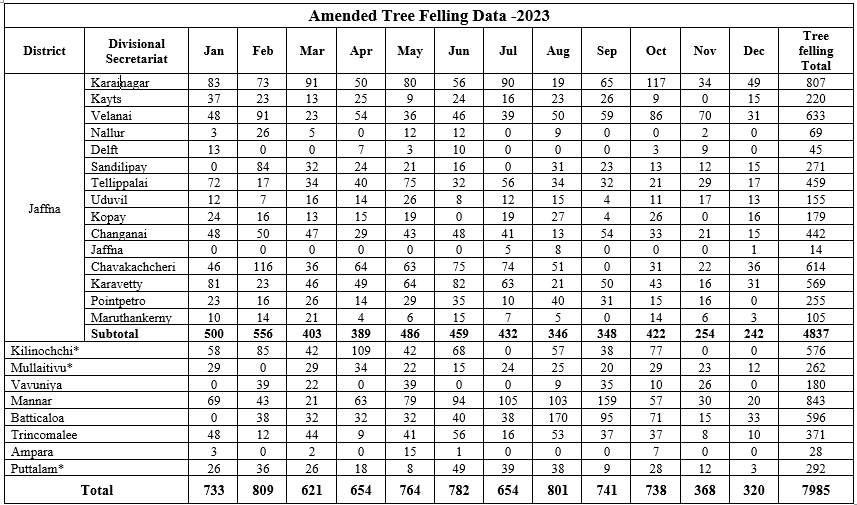
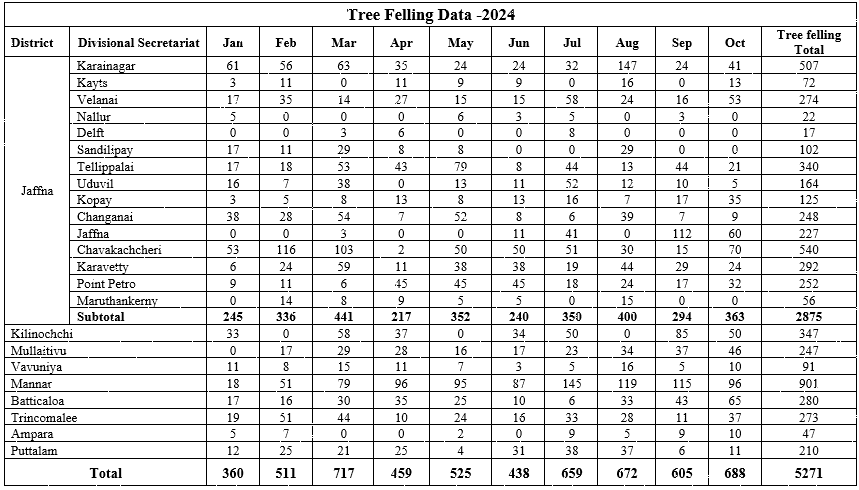
Control of Indiscriminate Tree Felling
Indiscriminate Palmyrah tree felling is a serious issue which is threatening the Palmyra industry. Palmyrah timber is a valuable products traditionally used for roofing in north and eastern provinces though unproductive mature trees are permitted to cut for timber purpose, emerging development needs such as road expansion, electricity supply, land cleaning housing schemes increase the demand for cutting trees.
By understanding the seriousness of this issue, Palmyra board is working closely with the divisional secretariats. Applications for tree cutting are checked by the field staff of PDB prior to granting approval. In addition to that, Palmyra board Reporting illegal tree felling cases to the police with the support of GN and DS. This control activity significantly reduces tree felling.
| Last Three Years Detail of Tree Cutting | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Districts | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 |
| Jaffna | 8,398 | 10,514 | 7,382 |
| Mannar | 1,187 | 1,189 | 1,232 |
| Vavuniya | 124 | 186 | 355 |
| Killinochchi | 658 | 1,391 | 846 |
| Mulaithivu | 351 | 844 | 823 |
| Trincomalee | 459 | 453 | 338 |
| Batticaloa | 555 | 564 | 342 |
| Ampara | 175 | 198 | 143 |
| Puttalam | 258 | - | - |
| Total | 12,165 | 15,339 | 11,461 |
Palmyrah Model Farms
Majority of the farm lands are government lands given by the divisional secretariats for the palmyrah plantation. These lands are planted with palmyrah seeds time to time and developed as model palmyrah plantations of PDB. Hence most of the lands are not suitable for agricultural crops few farms are intercropped with suitable crops.
As palmyrah palms are planted in a certain area in a systematic Mannar. It acts as a model for palmyrah industrialization. Further it acts as a demonstration unit for the public and it create awareness among the people to utilize their unproductive own land efficiently in such kind of farming. Model farms are a long term investment for the palmyrah industry. Therefore we can’t expect an income until maturity (15-20 Years). As most of the model farms given below are with young palmyrah trees it should be maintain properly to get better output in future. Anyhow reducing number of tappers or unavailability of tappers to working in this kind of plantations are the major short falls for the effective industrialization and maintenance of this farms.
| Details of the Model Farms | ||
|---|---|---|
| District | Location & Area | Main Crops |
| Jaffna | Mamunai | Palmyrah and Cashew |
| Delft | Young Palmyrah | |
| Kudaththanai | Young Palmyrah | |
| Vavuniya | Puliyankulam | Young Palmyrah, Lime |
| Killinochchi | Ootrupulam | Young Palmyrah, (5-10 years old) |
| Hambanthatta | Weerawila | Palmyrah and annual crops as banana, Gingily |
Other Activities
- Preparation and progress reporting of annual action plan
- Development and submission of project proposals for sectoral development,
- Preparation of annual reports.
- Sector data collection and reporting.
| District | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jaffna | 109,000 | 121,685 | 50,400 | 271,600 | 90,450 |
| Mannar | 89,221 | 81,600 | 55,000 | 52,520 | 14,150 |
| Vavuniya | 91,000 | 25,030 | 145,000 | 10,020 | nil |
| Kilinochchi | 12,500 | 41,900 | - | 7,500 | 11,000 |
| Mullaitivu | 27,750 | 74,700 | 125,000 | 3,750 | 32,000 |
| Trincomalee | 2,500 | 48,870 | - | 24,000 | nil |
| Batticaloa | 39,000 | 58,173 | 100,000 | 36,400 | 60,000 |
| Amparai | 10,000 | 10,000 | 25,000 | 78,600 | 20,000 |
| Hambanthota | - | - | - | - | 5,000 |
| Total | 380,971 | 461,958 | 500,400 | 484,390 | 232,600 |
GPS METHOD - JAFFNA DISTRICT
| No | Divisional Secretary Division | Palmyrah Tree Population |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Delft | 103,562 |
| 2 | Kayts | 63,582 |
| 3 | Velanai | 160,544 |
| 4 | Karainagar | 132,429 |
| 5 | Jaffna | 2,434 |
| 6 | Nallur | 39,871 |
| 7 | Thenmaradchi | 396,770 |
| 8 | Vadamaradchi South West | 114,542 |
| 9 | Vadamaradchi North | 87,634 |
| 10 | Valikamam South West | 100,962 |
| 11 | Valikamam East | 57,981 |
| 12 | Valikamam North | 89,111 |
| 13 | Valikamam South | 33,732 |
| 14 | Valikamam West | 125,229 |
| Total | 1,508,383 | |
| * One division could not be covered due to financial issue to purchase map | ||
Important Links
Contact Us
Mrs. S. Janarthanan. B.Sc (Agri), M.Sc (OM), LLB
Manager (Development)
Tel: 021 2222034
Fax: 0212224154
E-Mail: slpdbho@gmail.com